Since the industrial revolution, we have been using the linear economy model where we “take-make-use-dispose”. In other words, a linear economy takes raw natural resources, transforms them into products and then these products are disposed of after just a few uses.
This system has been creating billions of tonnes of waste across the world. However, a lot of this waste can be easily reused, shared, repaired or recycled. That’s what the idea of a circular economy entails.

The circular economy is a concept of production and consumption which involves sharing, reusing, recycling and repairing. This model intends to make products last longer by extending their life for as long as possible, reducing the waste to a minimum.
The whole vision of the circular economy is to minimise the use of natural resources to produce and maximise recycling and reusing. The circular economy model combines old strategies like reusing, reducing and recycling with new methods like renting things instead of owning. The idea of this model is not to end growth but to change our ways and blend our development with nature.
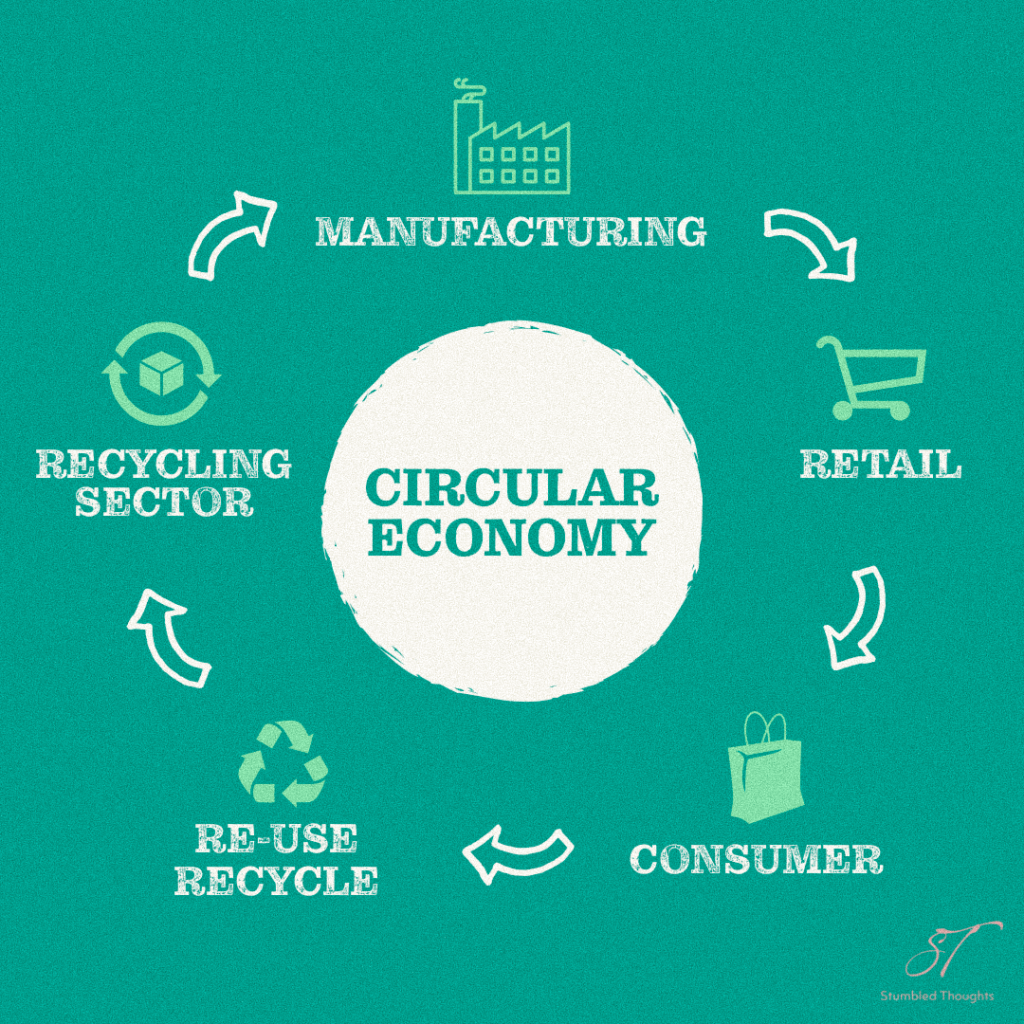
The circular economy is based on three aspects :
Minimal Waste & Pollution
In a circular economy, waste should not exist. Products are designed for reuse and can be disassembled. A vital component of a circular economy is to treat energy and resources as valuable and finite—single or limited uses of products to be eliminated. Waste is considered a design flaw. Introducing a “re-thinking” concept will help us explore new technologies, designs, and perspectives to make products last longer through refurbishment and reuse instead of throwing them away. It also means reducing recycling and disposal, which uses both energy and labour. An excellent example of a ‘re-thinking’ design concept is Gerrard Street , a company providing subscription-based services for its headphones. Their product can easily be repaired and disassembled with around 85% of the components that can be reused.
Regenerating Natural EcoSystem
Circular economy distinguishes between technical and biological cycles. Organic based materials are used in a way that can later be used to enhance our natural resources. In a circular economy, we take the example of nature which uses everything and wastes nothing. Organic or plant-based wastes can be used as fertilisers to enhance soil nutrients or regenerate the oceans that provide our renewable resources for the economy. Companies like Connect the Dots and The Balbo group are already working on regenerative agriculture and working with farmers to improve soil health and promote biodiversity.
Renewable Energy & Resources
Renewable energy can replace fossil fuels in a circular economy. At the same time, rental services and sharing businesses will serve more people with fewer products. Using less and decreasing our dependence on resources is one of the principles of this economy. The goal is to preserve finite natural raw materials by restricting their extraction and balancing the flow of renewable resources. The more we increase the extraction of resources, the more will be the consumption of energy, which will eventually increase the production of carbon emissions. Therefore in a circular economy, more thoughtful use of these resources is aimed to minimise carbon emissions. Iberdrola, a Spanish multinational company, generates, distributes, and trades clean energy. This clean energy is generated using wind, mini-hydro, solar thermal, photovoltaic, and biomass, making Iberdrola a good example of a circular economy.
Benefits of Circular Economy
Moving towards a circular economy will positively affect our planet’s ecosystem by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and preserving our natural resources. There will be no or minimal wastage. Renewable energy and resources will reduce our dependence on raw natural resources, providing energy-efficient and non-toxic products.
Using organic waste to regenerate our ecosystem will result in healthier soil and ecosystem. It will also prevent soil degradation.
Reusing and an efficient eco-design will also help companies reduce their costs and total annual greenhouse gas emissions.
A circular economy will help in reducing pressure on our environment. It will balance our ecosystem and economy, preserve our natural resources while leading to innovations and eventually to a better quality of life.

Linear and circular economy – excellent guide! Thank you 😊
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you!! 😊
LikeLiked by 1 person
You are welcome 😊
LikeLike